Climate change is an environmental problem that has a significant effect on the continued existence of life, including human beings, and efforts to prevent it are now a major challenge for the global community. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Group has positioned climate change initiatives as an important business issue and is promoting the reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions resulting from its business activities.
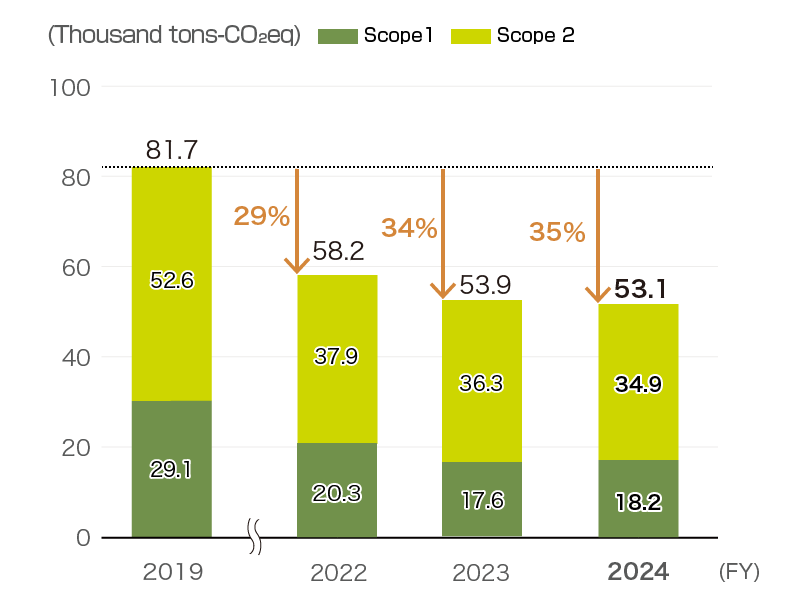
GHG emissions (Scope 1 + 2)
To mitigate climate change, the Group is endeavoring to reduce its energy consumption and GHG emissions by preventing the leakage of fluorocarbons, and has set the following targets in the Medium-Term Environmental Action Plan 21–25.
GHG emissions (Global: Scope 1 + 2)
58% reduction in GHG emissions by fiscal 2025 compared to 2019
GHG emissions for all global bases in fiscal 2024 were 53.1 thousand t-CO2eq, down 35% compared to fiscal 2019.
This breaks down as: Scope 1 emissions directly from combustion by the Group were 18.2 thousand t-CO2eq, a 37% reduction from fiscal 2019, with Scope 2 GHG emissions arising indirectly from the company due to use of electricity, etc., of 34.9 thousand t-CO2eq, a 34% reduction on fiscal 2019.
Additionally, we have concluded agreements to transition to purchasing power derived from renewable energy sources at our manufacturing bases in Japan (Onoda and Yoshitomi), and anticipate achieving our goal of a 58% reduction in fiscal 2025.
In the Group, Scope 3 GHG emissions were largest in category 1 (purchased goods and services), accounting for 95.8% of Scope 3. Category 1 is calculated using secondary data (purchase value) and increased 6.0% compared to the previous fiscal year. Going forward, we will strengthen engagement with suppliers and consider calculation methods that better reflect the actual state of emissions, and will promote the setting of Scope 3 reduction targets and the reduction of emissions.
Scope 3 GHG emissions
|
Category |
GHG emissions (Thousand t-CO2eq) |
Calculation method |
|
|
1 |
Purchased goods and services |
723.2 |
Calculated from the purchase prices of raw materials and products in Japan, which are multiplied by the emissions unit values from the Ministry of the Environment database* |
|
2 |
Capital goods |
17.1 |
Calculated from acquisition amounts of property, plant and equipment, for all consolidated companies in Japan and overseas, which are multiplied by the emissions unit values from Ministry of the Environment database* |
|
3 |
Fuel- and energy-related activities not included in Scope 1 or 2 |
9.0 |
Calculated from amount of energy used at Group offices in Japan and overseas, which is multiplied by emissions unit values from Ministry of the Environment database* or the emissions unit values from the LCI database (IDEAv2.3) |
|
4 |
Transport and delivery (upstream) |
2.3 |
Calculated from transportation ton-kilometers for shipments in Japan from plants to distribution centers, shipments from distribution centers to wholesalers, and shipments from sales-promotion item warehouses to branches, sales offices, etc., using the ton-kilometer method in the greenhouse gas emission calculation and reporting manual from Japan’s Ministry of the Environment and Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Calculated from electricity used for storage management at outsourced distribution centers and sales-promotion item warehouses, multiplied by the actual emissions factor indicated in the emissions factors for electric power enterprises announced by the Ministry of the Environment and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry on March 18, 2025 |
|
5 |
Waste generated in operations |
1.3 |
Calculated from the amounts of waste, by type, from Group offices in Japan (production and research bases, headquarters/Tokyo Head Office, distribution centers, and sales offices), which are multiplied by emissions unit value from Ministry of the Environment database* |
|
6 |
Business travel |
0.6 |
Calculated from number of employees in Japan and overseas, which is multiplied by the emissions unit value from Ministry of the Environment database* |
|
7 |
Employee commuting |
1.1 |
Calculated by multiplying the amount of transportation costs paid by transportation districts in Japan and overseas by multiplying the emissions unit values from Ministry of the Environment database* |
|
12 |
End-of-life treatment of sold products |
0.2 |
Calculated from amount of recycling obligation based on the Containers and Packaging Recycling Law in Japan, which is multiplied by the emissions unit value from Ministry of the Environment database* |
|
Total |
754.8 |
||
- Ministry of the Environment database: database on emissions unit values for calculating greenhouse gas emissions, etc., by organizations throughout the supply chain (Ver. 3.5)
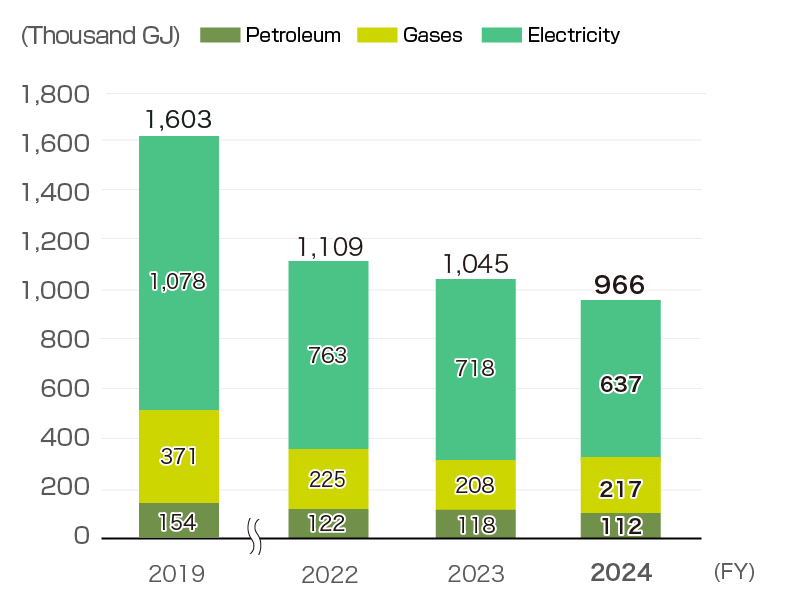
The Group in Japan holds energy liaison committee meetings to discuss energy use and conservation measures for each base and for the entire Group, and to achieve a common awareness of these with personnel responsible for energy at each base. We are also promoting energy conservation activities globally by creating energy management systems throughout the Group.
Each base is undertaking efforts directed at energy conservation, such as updating to high-efficiency equipment and switching to LED lighting, installing automatic sensor-based lighting controls, and shutting off air conditioning in manufacturing areas during extended vacations. Additionally, we are conducting a company-wide energy conservation campaign to raise employee awareness in this regard and promoting activities such as turning off lighting, air conditioning, and office equipment during lunch breaks, encouraging people to use the stairs, and adopting paperless business practices, all of which can be implemented throughout the company on a daily basis.
Energy use (global)

- 拡大
- Energy conservation campaign poster
The Group has created a roadmap for the carbon neutrality action plan (introduction of renewable energy, switching to next-generation vehicles, fuel conversion for boilers, etc.), and is promoting carbon neutrality.
Use of renewable energy that does not cause GHG emissions is an effective measure against climate change.
We are switching to purchasing power for our production bases in Japan (Onoda and Yoshitomi) to power derived from renewable energy sources, and from fiscal 2025 will introduce zero-carbon power. The Group is deploying solar power generating equipment at the Hyangnam Factory in Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Korea and is introducing electricity from renewable energy sources in the Shonan, Onoda, and Yoshitomi offices, as well as some offices in Europe. Going forward, we will also consider using electricity from renewable sources at other bases.
The Group is shifting steadily from gasoline-powered vehicles to hybrid vehicles and promoting eco-driving to reduce GHG emissions from company-owned vehicles (switch to hybrid vehicles planned for completion by fiscal 2027). Additionally, we are currently evaluating switching to EVs in conjunction with the switch to hybrid vehicles.
|
FY2019 (Base year) |
FY2022 |
FY2023 |
FY2024 |
||
|
Ratio of company-owned vehicles that are hybrid vehicles |
67% |
67% |
70% |
82% |
|
|
CO2 emissions from company-owned vehicle fuels (Japan) |
CO2 emissions |
4,165 t-CO2 |
3,520 t-CO2 |
3,596 t-CO2 |
3,145 t-CO2 |
|
Ratio of reduction in CO2 emissions (compared to fiscal 2019) |
ー |
15% |
14% |
24% |
|
Environmentally friendly actions in fiscal 2024
Support for environmentally friendly products
We have adopted biomass plastic blister packages as our first environmentally friendly packaging material. These blister packages* allow us to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 30–70% compared to blister packages made from oil-derived plastic.
* Blister package: Also known as press-through package (PTP) in Japan. See below for details.
The Group is working to prevent leaks of fluorocarbons, which add to the effects of ozone layer depletion and greenhouse gases. Equipment containing fluorocarbons installed in bases in Japan is properly managed with a ledger in accordance with the revised Law Concerning the Discharge and Control of Fluorocarbons. In addition, we comply with installation standards and conduct regular equipment inspections and when disposing of the equipment, we recover and destroy the fluorocarbons and maintain a record of this for three years.
Furthermore, when installing equipment containing fluorocarbons, we select a model that takes into account global warming potential and energy-saving performance.
In fiscal 2024, at production and research bases in Japan, the amount of fluorocarbon leakage was 160 kg (649 t-CO2 equivalent). The amount of fluorocarbon leakage for Group companies in Japan has been below the threshold for reporting to regulatory authorities for all years since 2015 when the leakage reporting system was established.
Note: Information on this page pertains to activities and results for fiscal 2024.