Water shortages and increased flood risks due to climate change are becoming a social issue, and for Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Group, securing good quality water is extremely important for pharmaceutical research and manufacturing.
The Group has set a goal in Medium-Term Environmental Action Plan 21–25 of reducing the volume of water usage, and manages the volume of water usage and the volume of wastewater in its business activities, saves water to reduce the volume of water usage, and makes effective use of its limited water resources.
Volume of water usage reduction target (Global)
Reduce volume of water usage 15% from fiscal 2019 by fiscal 2025
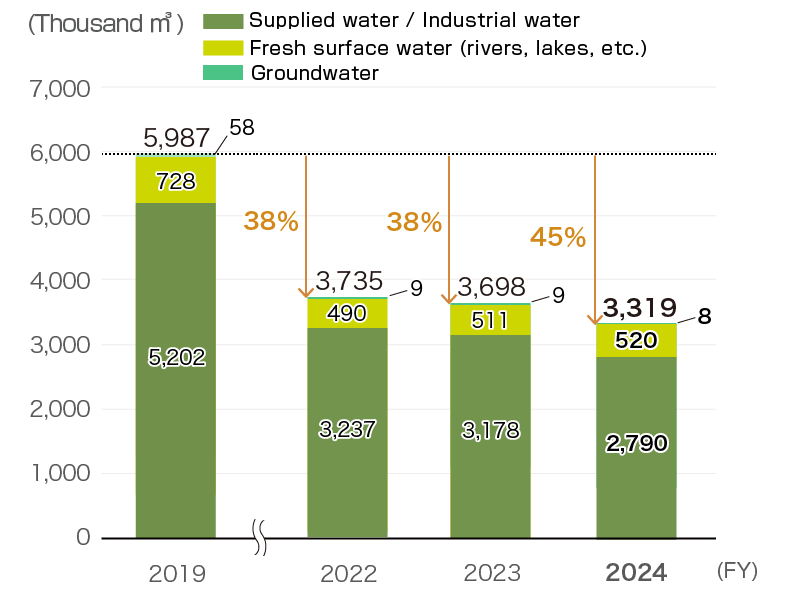
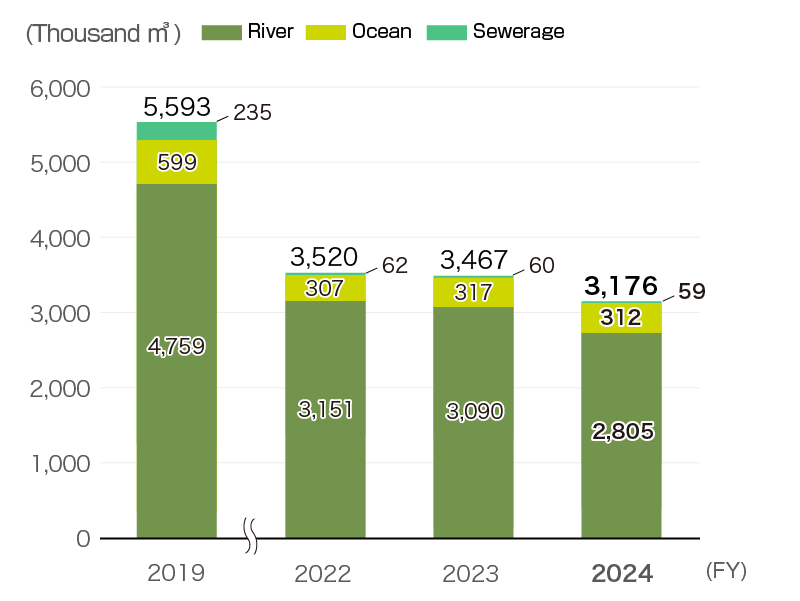
The volume of water usage of all bases globally in fiscal 2024 was 3,319 thousand m3, down 45% from actual withdrawals in fiscal 2019, significantly exceeding targets. In addition to our everyday water-saving activities, the use of recycled water at our plants and a review of water intake reduced the volume of water usage. The total volume of wastewater at all bases globally was 3,176 thousand m3, mainly discharged to rivers.
Volume of water usage (global)
Volume of wastewater (global)
In recent years, the impact of climate change has increased the risks such as water resource depletion, flooding, and storm surges. The Group utilizes the “Aqueduct” water risk assessment tool from the World Resources Institute (WRI) to conduct assessments of water risk at production and research bases in Japan and overseas. Additionally, we conduct hearings and environmental audits at each base and check risks. As a result of these risk assessments, an overseas production base in Indonesia was deemed to be a high risk, but we are monitoring the situation onsite while taking appropriate measures as required.
|
Business locations |
Water stress assessment |
Future water stress changes |
|
Yokohama Office |
Medium–High (20–40%) |
No major changes until 2080 |
|
Shonan Office |
Medium–High (20–40%) |
|
|
Onoda Office, Onoda Plant |
Low–Medium (10–20%) |
|
|
Yoshitomi Plant |
Low–Medium (10–20%) |
|
|
Hyangnam Plant (Korea) |
Medium–High (20–40%) |
|
|
Hsinchu Plant (Taiwan) |
Low–Medium (10–20%) |
|
|
Bandung Plant (Indonesia) |
High (40–80%) |
Note: Information on this page pertains to activities and results for fiscal 2024.